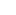Definition and Technology
Slewing-ring:
Definition
The slewing-ring is normally composed of two rings made of high résistance steel, and their relative rotating motion is allowed by the creation of raceways hosting the rolling elements, which can be balls or cylindrical rollers.
The roller raceways are the structural heart of the bearing and require the major attention during the production cycle.
An induction hardening treatment must be applied on raceways in order to increase their hardness both on the surface and in depth. This allows the bearing to endure the huge loads it is usually subject to, ensuring structural integrity over time.
Components :
|
External and internal ring: Slewing-rings are manufactured either with carbon steel, such as CR45 or alloy steels such as 42CrMo4 (see details in chapter technology). |
|
|
Rolling elements: DIN5401 balls are used for four point contact bearings while DIN5402 cylindrical rollers are used for crossed roller bearings: both types of rolling elements are mode of 100 Cr6 material. |
|
| Spacers: Nylon spacers are used to guide the rolling elements, to hold them at an equal distance from each other and to prevent them from coming into contact with each other. | |
| Sealing : Seals made from NBR rubber protect the gap in the bearing on both sides from the ingress of dirt, dust and moisture. Please note that a correct lubrication increases the effectiveness of the seals (see Raceway Lubrication chapter) |  |
|
Greasers : Slewing-rings are delivered with an initial lubrication of raceways and gear, using grease listed in the Installation and Maintenance catalog. Strictly follow the instructions supplied in order to preserve the life cycle of the bearing. |
 |
| Bouchon (P) = bouchon de remplissage des billes et raccord de trempe du chemin de roulement. |
Technology
Rings material:
The materials used to produce slew bearings can be carbon steel, as C45, or alloy steel, as 42CrMo4. The choice between these two types of steel is related to the required mechanical performances, like core-tenacity and hardness, but also to other technological factors, as hardenability. The 42CrMo4 allows a deeper thickness of the hardened layer than C45, ensuring higher load capacity. The C45 (or equivalent) is the material used for the production of the major part of standard medium- low diameter bearing, the 42CrMo4 is used for medium-high diameters, and for many different special applications.
After forging and ring mill, a heat treatment, either core-hardening or normalization, must be applied in order to increase all mechanical proprieties of the material, such as tensile strength, tenacity, hardness. The core-hardening process, composed by a succession of quenching and tempering heat treatments, confers to the material higher hardness and higher core-resistance values than normalization, proprieties required in case of heavy stress conditions on the gear.
Induction hardening of the raceways:
The heat treatment of raceways, increasing the hardness value on surface and in depth up to a value range of 55 4- 62 HRC, involves a higher load capacity of the bearing and avoid plastic deformation along rollers contact points. This heat treatment consists in bringing a copper made inductor crossed by high amperage alternate current nearer to the raceways. The proximity of magnetic field to the metallic raceway inducts parasite currents and Joule effect that produces an instantaneous heating of interested regions leading to the austenite temperature field. The following quick cooling produces the formation of martensite and carbides. The choice of carbon steel, as C45, as well as an alloy steel, as 42CrMo4, allows to obtaining best metallurgical results during this process.
Note : The soft spot is a raceway point that has not been induction hardened, due the fact at the end of hardening process it isn't possible to overlay the hardening ends, the risk is to generate cracks or directly to produce the breaking of the piece. For the un-toothed ring is a common rule to make the soft spot coincident with the filling plug, the inserting point of roller elements, machined together to the raceways. In order to identify the soft spot on the geared ring it is necessary to stamp a "S" letter on the upper surface of the bearing, in corresponding position.
Induction hardening of the gear :
The standard surface hardness of core-hardened steel used for bearing could be 30 HRC at maximum (42CrMo4). This value of hardness could not be enough to preserve the lifetime of the gear in some applications. A high rotational torque producing a high load (and friction) on the tooth, high rotational speed, heavy duty environmental condition including dust and abrasive elements, or the necessity to extend the lifecycle of the bearing to the maximum, any of those aspects may require a gear induction hardening. The heat treatment could be only flank or flank & root of the teeth, according to loads and application type, and it leads the surface hardness value to a maximum value of about 60 HRC.
Clearance type :
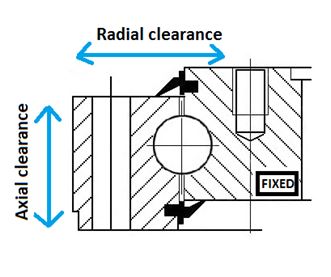
Clearance of a slew bearing is the measure of the
motion freedom of the outer ring compared to the inner ring (and vice versa), evaluated in two directions: along the axial direction, defined by the revolution axis of the bearing, and along radial direction, any direction perpendicular to the first one when assembling, the plays of the bearing is determined by matching rings raceways with rollers, each component having its tolerance. The slew-bearing can show four different types of clearances, both bail and crossed roller bearing. The type choice id done simultaneously to bearing type selection, and mainly depends on the application field.
|
Standard Clearance 3a, 3r 0,1o 4- 0,35 mm Usually in a slewing-ring axial and radial clearance can vary from 0,1 to 0,4 mm. Pilots are in function of application and/or type of bearings: on standard balls series, for example, pilots |
 |
|
Reduced Clearance 9a, dr —>► o h- o, lo mm When the application requires the maximum precision during operation, with high values of rotational speed, the slew bearing design changes in favor of a reduction of axial and radial plays. Clearance can vary from null value to few hundreds of millimeter, in positive value. Precision series adopt general dimensions of standard series and show pilots on both rings |
 |
|
Slightpreload da, 3r —► 0 4- - 0,03mm When the application requires the absence of any plays, radial and axial, in order for example to avoid any positional error or because the bearing works in vertical position, the clearance is eliminated and the construction is called "with preload". When the condition is slight preload the design interference between rollers and raceways can vary from zero to few hundreds of millimeter: the slewing-ring shows anyway an adequate rotational speed, even on intense operational cycles, with a limited friction torque. This type of construction is not standard and must be specifically requested. |
 |
|
Preload 3a,ô,—►<- 0,03 mm When load conditions includes relevant tilting moments that may quickly invert their direction and the eventual presence of vibration which involves raceways, the slewing-ring construction must be strongly preloaded. Interference range shows only negative values |
 |
Surface protection system:
The external surface protection treatment protects metallic surfaces from their oxidation caused by atmospherically or chemical agents, during operational lifetime or simply during the storage period.
We can apply the following different surface protection treatments, according to your needs.
There are several types of protection:
1 - Protective oil:
All slewing-rings are protected with applying oil to surfaces, seals and gear. It allows a constant protection for about 1year.

2 - Painted :
Exposed surfaces can be protected by painting, on customer request.

3 - Zinc based galvanized coating (on request):
In case of atmospheric or chemical agents a Fe-Zn galvanized layer can be applied. The thickness is just few hundreds of mm but it allows a durable protection with its typical iridescent yellow color.

4 - Hotflame spray zinc coating (on request):
This treatment can apply a protective layer up to 3 ten of millimeter thickness. It resists to any type of atmospheric agent and also to abrasive action on surface.